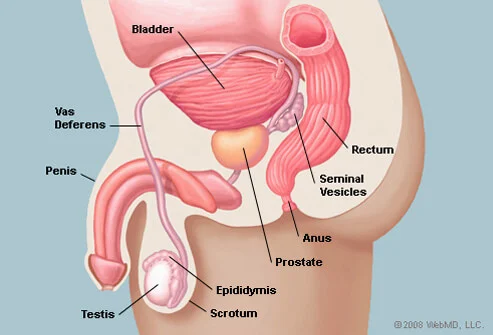
Prostate problems are a common concern for men, especially as they get older. The prostate is a small gland located in the male reproductive system that produces fluid that is added to sperm during ejaculation.
Prostate problems symtoms
The symptoms of prostate problems may vary depending on the specific condition. Some common symptoms of prostate problems include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting and stopping urination
- Weak urine flow
- Pain or discomfort during urination or ejaculation
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Pain in the lower abdomen or lower back
It is important to note that these symptoms may also be caused by other conditions, such as a urinary tract infection. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider for a proper evaluation and treatment. Prostate problems, if left untreated, can lead to serious complications, such as kidney damage or bladder infection.
Prostate problems lead to more trouble
Prostate problems may include:
- Enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH): This is a common condition that occurs when the prostate gland becomes enlarged. BPH is not cancerous, but it can cause urinary symptoms, such as frequent urination, difficulty starting and stopping urination, and weak urine flow.
- Prostate infection (prostatitis): This is an infection or inflammation of the prostate gland that can cause urinary symptoms, pain in the lower abdomen or lower back, and pain during ejaculation.
- Prostate cancer: This is a type of cancer that occurs when abnormal cells grow out of control in the prostate gland. Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, and it is usually slow-growing.
Why prostate becomes a problem?
The root causes of prostate problems are not fully understood, but a variety of factors may contribute to their development, including:
- Age: The risk of prostate problems increases with age.
- Family history: A family history of prostate problems or prostate cancer may increase the risk of developing these conditions.
- Diet: A diet high in saturated fat and low in fruits and vegetables may increase the risk of prostate problems.
- Lifestyle factors: Lack of physical activity, stress, and poor sleep may increase the risk of prostate problems.
- Vitamin and mineral deficiencies: Deficiencies in certain vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin D and zinc, may contribute to the development of prostate problems.
Prostate problem treatment
Treatment for prostate problems may include lifestyle changes, such as exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, and managing stress, as well as taking supplements or medications. The specific treatment will depend on the type and severity of the prostate problem.
For BPH, treatment may include medications that relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder or surgery to remove part of the prostate gland.
For prostatitis, treatment may include antibiotics to clear the infection and pain medication to relieve discomfort.
For prostate cancer, treatment may include surgery to remove the prostate gland, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
It is important to speak with a healthcare provider for a proper evaluation and treatment of prostate problems. They can help determine the best course of treatment based on your individual needs and medical history.