Premature ejaculation (PE) is a common sexual dysfunction that refers to a man ejaculating too quickly during sexual activity. It is generally defined as ejaculating within one minute of penetration. PE can be a frustrating and distressing problem for both the man and his partner, and it can have a negative impact on the man’s self-esteem and the couple’s relationship.
Causes of premature ejaculation
There is limited scientific research on the specific causes of PE, but it is thought to be a complex interaction of physical, psychological, and relational factors. Some potential contributing factors that have been identified include:
- Lifestyle factors: certain lifestyle behaviors, such as smoking and obesity, may be associated with an increased risk of PE.
- Psychological factors: stress, anxiety, and depression may contribute to PE, as well as negative attitudes or beliefs about sex.
- Relationship factors: conflicts or difficulties in the relationship, or a lack of intimacy and communication, may contribute to PE.
- Biological factors: certain medical conditions, such as hormonal imbalances or problems with nerve function, may be associated with PE.
- Lack of sleep: sleep deprivation may contribute to PE, as it can affect physical and psychological functioning.

It is important to note that the specific causes of PE can vary from person to person, and it is often a combination of multiple factors. If you are experiencing PE and are concerned about it, it is recommended that you speak with a healthcare provider for further evaluation and treatment options.
Vitamins and supplements that can help with premature ejaculation
While there is no specific vitamin or mineral that has been proven to treat PE, there are some nutrients that may help improve sexual function in men. These include:
- Zinc: This mineral is important for the production of testosterone, which plays a role in sexual function and desire. Zinc can be found in foods like oysters, red meat, poultry, and beans.
- Vitamin D: This vitamin is important for maintaining healthy testosterone levels and has been shown to improve sexual function in men. Vitamin D can be found in fatty fish, eggs, and fortified foods.
- B vitamins: B vitamins, particularly B-12 and folic acid, are important for maintaining energy levels and supporting healthy nerve function. These vitamins can be found in foods like poultry, eggs, and leafy green vegetables.
- L-arginine: This amino acid is important for maintaining healthy blood flow, which is important for sexual function. L-arginine can be found in foods like nuts, seeds, and poultry.
It’s important to note that while these nutrients may have some potential benefits for sexual function, they should not be used as a replacement for medical treatment. If you are experiencing premature ejaculation, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
How condom size is relevant to premature ejaculation and quality of sex
Condom size can affect sexual performance and potentially contribute to premature ejaculation in a few ways.
- Tight condoms: Wearing a condom that is too tight can restrict blood flow to the penis, leading to difficulty achieving and maintaining an erection. This can also make it more difficult to control ejaculation and may lead to premature ejaculation.
- Loose condoms: On the other hand, wearing a condom that is too loose may cause the condom to slip off during intercourse, which can lead to condom failure and an increased risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unintended pregnancy. This can also lead to a decrease in sexual pleasure and potentially contribute to premature ejaculation.
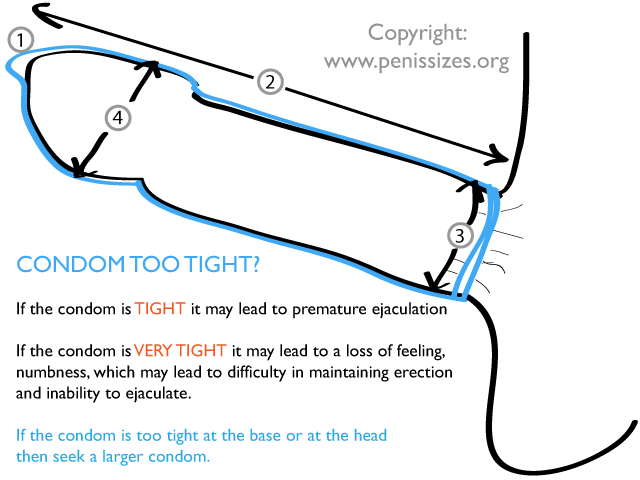
It’s important to use condoms that fit properly to ensure maximum effectiveness and pleasure. If you are unsure of your condom size, you can try different sizes or consult a healthcare provider or pharmacist for guidance.
Finding the right condom and using the condom correctly
Using the right condom and using it correctly can help prevent premature ejaculation in a few ways:
- Find the right size: Condoms come in different sizes to fit different penis sizes. It’s important to find a condom that fits properly to ensure maximum effectiveness and pleasure. If you are unsure of your condom size, you can try different sizes or consult a healthcare provider or pharmacist for guidance.
- Roll the condom all the way down to the base of the penis: This helps to ensure that the condom stays in place and covers the entire penis, reducing the risk of condom failure. It can also help to lessen the pressure on the arteries, which may help to improve blood flow to the penis and potentially improve sexual performance.
- Check the expiration date: Make sure to check the expiration date on the condom packaging before using it. Using an expired condom can increase the risk of condom failure.
- Store condoms properly: Condoms should be stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Avoid storing condoms in hot or humid environments, as this can weaken the latex and increase the risk of condom failure.
- Use a new condom for each sexual act: It’s important to use a new condom for each sexual act to reduce the risk of condom failure and STIs.
By following these tips, you can help ensure that you are using condoms correctly and effectively. It’s also important to communicate with your partner about condom use and to practice safe sex to reduce the risk of unintended pregnancy and STIs. Keep in mind that while using the right condom and using it correctly may help to improve sexual performance and potentially prevent premature ejaculation, it is not a substitute for medical treatment. If you are experiencing premature ejaculation, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.